
Table of Contents
Overview of variable resistors
The variable resistor’s resistance is variable, as the name implies. A variable resistor’s resistance can be easily varied or changed to the desired value. Variable resistors are commonly employed when the user is unsure of the exact resistance value he needs.
Resistance is the process of limiting or restricting electric current to a specific level. The resistor is a device that is used to limit the passage of electric current to a specific level.Variable resistors are devices that not only restrict the flow of electric current but also control (raise and decrease) the flow of electric current.
When we increase the resistance of a variable resistor, the electric current flowing through the variable resistor decreases. Similarly, increasing the resistance of a variable resistor to a lower resistance value increases the electric current flowing through the variable resistor.
Definition of variable resistor
A variable resistor is a resistor that controls (increases or decreases) the flow of electric current when its resistance is varied or changed. In other words, as we change the resistance of the variable resistor, the electric current passing through it changes.
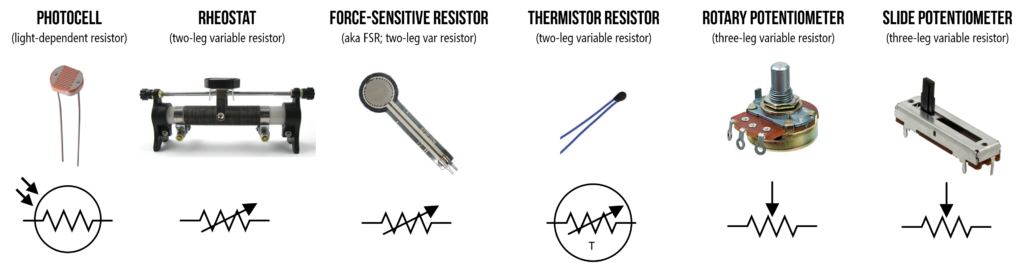
Variable Resistance
Variable resistors are intended for use in applications where the equipment used needs to modify the resistance often, such as tone, volume, focus, and brightness settings. A potentiometer and a rheostat are the two most common forms of variable resistors. The volume control on your radio is an example of a potentiometer, and the dimmer control for the dash lights in an automobile is an example of a rheostat. There is a minor distinction between them. Rheostats typically have two fixed and one moveable connection.

A rheostat is technically any variable resistor. The potentiometer always has three connections, two of which are fixed and one of which is movable. In general, rheostats have a narrow range of values and a high current handling capacity. Although the potentiometer has a large range of values, it often has limited current handling capability. Potentiometers are commonly used as voltage dividers.
Potentiometer
View A of the diagram below shows an example of a potentiometer. Potentiometers are constructed using either composition or wire-wound resistance elements, and the same principles that apply to fixed resistors with those types of components apply to potentiometers.
Thermistor
The term thermistor is derived from the phrases thermal and resistor. It is a sort of resistor whose resistance changes as the temperature changes around it.
Negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistors and positive temperature coefficient (PTC) thermistors are the two types of thermistors. The resistance of NTC thermistors lowers as temperature rises, whereas the resistance of PTC thermistors rises as temperature rises.

Magneto resistance
Photoresistor
When a magnetic field is supplied to a magneto resistor, its resistance changes. When the magnetic field intensity delivered to the magneto resistor is increased, so is the resistance of the magneto resistor. Similarly, as the strength of the magnetic field delivered to the magneto resistor is reduced, so is the resistance of the magneto resistor.
The term photoresistor is formed from the phrases photon and resistor. The photoresistor’s resistance varies as light energy is applied to it. When the intensity of the applied light increases, the resistance of the photoresistor decreases. Photoresistors are classified into two sorts based on the substance used to make them: intrinsic and extrinsic photoresistors. When the intensity of the applied light increases, the resistance of the photoresistor decreases.
Light-dependent resistors, semiconductor photoresistors, and photoconductors are other names for photoresistors.

History
The term humistor is derived from the words humidity and resistor. Humistors are extremely sensitive to humidity. The humistor’s resistance varies with variations in the humidity of the surrounding air. Humistors are also known as humidity-sensitive resistors or resistive humidity sensors.
Force sensitive resistors
Resistors that respond to force
The name implies that force-sensitive resistors are extremely sensitive to the applied force. When we apply force to the force-sensitive resistor, the resistance rapidly changes. Force-sensitive resistors (FSR) are also known as force sensors, pressure sensors, force-sensing resistors, or force-sensing resistors (FSR).
Definition of wire wound resistor
A wire wound resistor is a passive component that uses metal wires to limit or restrict the flow of electric current to a specific level.
Wire-wrapped resistor construction
Winding metal wire around a metal core creates a wire-wound resistor. The metal wire serves as the resistance element in wire wound resistors, whereas metal core serves as the non-conductive substance.
Metal wires made of nichrome or manganin are often employed because they have a strong resistance to electric current and can work at high temperatures. Plastic, fiberglass, and ceramic are the most often utilised core materials.The metal wire’s resistance
The resistivity of the metal wire is directly proportional to the resistance of the wire wound resistor.
A high-resistance metal wire resists or blocks a substantial quantity of electric current. As a result, the wire wound resistor has a high resistance to electric current.A metal wire with low resistance, on the other hand, blocks a small quantity of electric current. As a result, the wire wound resistor has a low resistance to electric current.

Leave a Reply